The approach of the end of the year seems a good time to sum up thoughts. My comments here will not be news to regular readers, but may be to others. Also, this exercise is helpful for me to keep my thoughts clear. (I also expect to take next week off, so you won't be hearing from me for a while.)
Most of my work for the last several years has been focused on ways to reduce before tax inequality by reducing the amount of before-tax income that goes to those at the top of the income distribution. For better or worse, there don't seem to be a lot of progressives that share this beat. There are a few points that are worth making.
First, my focus on reducing income at the top doesn't mean for a second that I don't see efforts at raising income for those at the bottom (and middle) as being important. I have long been involved with or worked alongside people trying to raise minimum wages, protect or increase Social Security benefits, and increase unionization rates.
These are very important efforts, but at the end of the day, our ability to raise incomes at the middle and bottom will depend on reducing incomes at the top. This gets to the old pie-cutting story. If we want those at the middle and bottom to have much bigger slices of the pie, the folks at the top will have to get by with smaller slices.
To see how skewed the pie eating has gotten, if the federal minimum wage had kept pace with productivity growth since 1968, as it did from its establishment in 1938 until 1968, it would be $24 an hour today. That means a single full-time minimum wage earner would have an income of $48,000 a year. A two-earner couple getting the minimum wage would have an income of $96,000 a year.
This is a striking counter-factual, but we can't just go from here to there. In order for the economy to allow for this sort income and consumption by those at the middle and bottom, we have to reduce income and consumption at the top.
We can talk about expanding the pie, but I don't think that I, or anyone else, has a magical formula to hugely expand the size of the pie. There are areas where better policy can lead to a more productive economy, but we are more likely talking about one to two percent rather than ten to twenty percent, and even these gains are likely to be a long-term story, not gains we can see in two or three years.
It is also worth focusing on what pie-eating among the top means. There are many progressives who have made a sport of highlighting the enormous wealth that Jeff Bezos, Mark Zuckerberg, and other super-rich types have accrued from recent stock market gains. While the wealth of the super-rich is obscene, reducing these fortunes will actually not free up much room for more income lower down the ladder.
As a practical matter, Jeff Bezos and Mark Zuckerberg probably don't consume much more in a given year than your average single-digit billionaire. This means that if we took away $100 billion from each of them, it would not free up much consumption for those at the bottom. If we want to create the economic space to substantially expand incomes at the middle and the bottom, we will have to substantially reduce the consumption of not just some tiny segment of super-rich people, but also the rest of the top one percent and even the top five percent. (That gets us a cutoff in household income of around $300,000.) We might even have to knock down the income a bit of the next five percent (cutoff of household income around $200,000).
There is the political issue of the enormous influence that the super-rich can buy with their wealth. This is a huge problem, but it is best addressed in the near-term by increasing the opportunities for ordinary people to have a voice.
I know many on the left want to use taxes to reduce the income, and therefore consumption, of those at the top. While we can and should make our tax system more progressive, there are real limits on how far we can push progressive taxation. Rich people don't like to pay taxes. They can and do find ways to avoid and evade taxes. Insofar as they are successful in these efforts, we fail to reduce their income in the way intended, we create a huge tax-gaming industry, which is a source of economic waste and itself a generator of inequality, and we undermine faith in the system.
It is far better if we change economic structures in ways that don't allow people to get so rich in the first place. As a political matter, it is hard to defend an institutional structure that is both inefficient and a large generator inequality. As a practical matter, it is much easier to design systems that don't give rich people billions of dollars in the first place, than to try to impose taxes that pull most of their billions back after the fact.
This is the basis of my thinking in much of my work. I lay out the case most completely in Rigged (it's free), but I am constantly looking for new areas where altering rules can lead to less inequality, without jeopardizing efficiency.
Patent and Copyright Monopolies
I like to begin with patent and copyright monopolies both because this is the clearest case, and also because the most money is at stake. The basic point is painfully simple: patent and copyright monopolies are not intrinsic to the market, they are government policies designed to promote innovation and creative work.
As policies, they can be altered as we choose. They can be shorter or longer, stronger or weaker. We also can use other mechanisms to promote innovation and creative work.
These policies transfer an enormous amount of income from the bulk of the population to those in a position to benefit from patent and copyright monopolies. I calculated that these policies may transfer over $1 trillion a year from the rest of us to the beneficiaries of patent and copyright monopolies. This is an amount that is larger than the military budget, it is close to half of all before-tax corporate profits. In other words, it is real money.
Prescription drugs are the largest single chunk of this sum. Drugs are important, not only because of the money involved, but also because people's lives and health are at stake. The drugs that sell for tens, or even hundreds, of thousands of dollars would almost invariably be cheap in a world without patent monopolies and related protections. While any price is expensive for the poor, for most people, paying for drugs would not be a big problem if they sold for ten or fifteen dollars per prescription. Doctors could freely prescribe what they view as the best drug for their patients, without regard to price. (We need to make sure that government programs pick up the tab for the poor.)
There is also the issue of the perverse incentives created by patent monopolies. Drug companies routinely misrepresent the safety and effectiveness of their drugs to maximize their sales and therefore the benefit of monopoly pricing. The most extreme case (which no one ever talks about) is the opioid crisis, which was worsened as a result of drug companies widely pushing drugs that they knew to be more addictive than claimed.
The inequality story is also straightforward. Dishwashers and custodians don't benefit from patent monopolies. A very limited group of workers are in a position to get big gains from these policies. Bill Gates would likely still be working for a living if not for the patent and copyright monopolies on Microsoft software. When economists say that "technology" has increased the returns to education and inequality, they actually mean that patent and copyright monopolies have increased the returns to education and inequality, but it sounds much better to blame inequality on an abstract force than government policy.
The Corruption of Corporate Governance
There is a simple point here that seems to largely escape people on the left. CEOs are not worth their $20 million paychecks. That is not a moral assessment of the value of their work, that is a dollar and cents calculation about their value to the companies that employ them.
At this point there is a considerable body of research that shows the pay of CEOs is not closely related to the returns they provide to shareholders. Bebchek and Fried have a somewhat dated collection of research on the topic. I reference some more recent material in chapter 6 of Rigged. A couple of years ago, Jessica Schieder and I also contributed a piece to this literature.
The fact that CEOs are not worth their pay matters because it means that they are effectively ripping off the companies for which they work. There is a widely held view, that in recent decades, companies have been run to maximize returns to shareholders. However, if CEOs have been earning huge paychecks at the expense of the companies they work for, then it is not the case that companies are being run to maximize returns to shareholders.
The fact that returns to shareholders have not been high by historical standards over the last two decades supports the view that CEOs are not maximizing returns to shareholders. It is also worth noting that the shift of income from labor to capital only explains about 10 percent of the upward redistribution of the last four decades.
The fact that CEOs might be gaining at the expense of shareholders is not just a question of which group of rich people get the money. At the most basic level, there is reason to prefer the marginal dollar goes to shareholders, since even with the enormous skewing stock ownership, a substantial portion of shares are owned by middle class people in their 401(k)s and pension funds. By contrast, every dollar going to a CEO is going to someone in the top 0.001 percent of the income distribution.
But more importantly, the bloated pay of CEOs has a huge impact on pays scales throughout the economy. If the CEO is getting $20 million then it is likely the chief financial officer and other top tier executives are getting close to $10 million. And the third tier can be getting $2 or $3 million. By contrast, if we had the pay scales of forty years ago, the CEO would be getting $2 to $3 million. The second tier would be correspondingly lower, and the third tier may not even crack $1 million. The excess pay at the top in the corporate sector also leads to bloated pay for top executives in universities and private charities. And, with all this money going to the top, there is less for everyone else.
Anyhow, it should be apparent both that lowering the pay for CEOs will be a huge step in reducing income inequality, and that shareholders should be allies in this battle. Changing the rules of corporate governance (these are set by the government) to give shareholders more control over CEO pay can lead to lower pay at the top and therefore less inequality.
Globalization is a Policy, not an Exogenous Event
A popular story among elite types is that we can't have good-paying factory jobs that can support a family because of globalization. The deal is that workers earning $30 an hour, plus benefits, can't compete with workers in places like Mexico and China, who can do the same work for less than one-tenth as much.
This is true. But the fact that our factory workers were put in direct competition with low paid workers in the developing world was not just something that happened, it was the result of deliberate policy. Our trade deals were designed to make it as easy as possible for U.S. corporations to outsource work to developing countries and bring manufactured goods back into the United States. The massive loss of manufacturing jobs in the years from 2000 to 2007 (pre-Great Recession) was not an accident, that was the point of our trade deals.
We could have constructed our trade deals differently. Instead of putting manufacturing workers in competition with their counterparts in the developing world, we could have designed our trade deals to put doctors, dentists and other highly paid professionals in direct competition with their counterparts in the developing world. This would have meant standardizing licensing requirements in ways that ensured safety standards, while making it as easy as possible for foreign professionals to train to meet these standards and then practice freely in the United States.
While doctors are not among the super-rich, their average pay is close to $280,000a year, putting them in the top two percent of wage earners. They also earn roughly $100,000 more annually than their counterparts in other wealthy countries. If we got doctors' pay down to the levels in Germany or France, it would save us close to $100 billion a year. That comes to $700 per year per household.
When I have raised this issue with other progressives, many first dispute the idea that we could get foreign doctors that meet our standards. When I convince them of the absurdity of this position (there are plenty of very smart people in places like Mexico and India who would be happy to train to our standards for the opportunity to practice medicine here), they often respond with comments like people like their doctors or that they personally like their doctor.
I get that, but there is some serious logic missing. I like the person who cuts my hair; she doesn't earn $280,000 a year. Essentially, these progressive types are expressing class solidarity with very highly paid professionals. They are welcome to do so, although it is an odd position for people who consider themselves progressive, but there is a more fundamental and simple point at stake.
The fact that autoworkers have to compete with low-paid workers in the developing world, and doctors don't, is a political choice. This was not the result of an exorable process of globalization, it was the result of how policy types chose to structure globalization. No one should be surprised if manufacturing workers, and workers without college degrees more generally, who have been hurt by the loss of good-paying manufacturing jobs, are resentful of this decision.
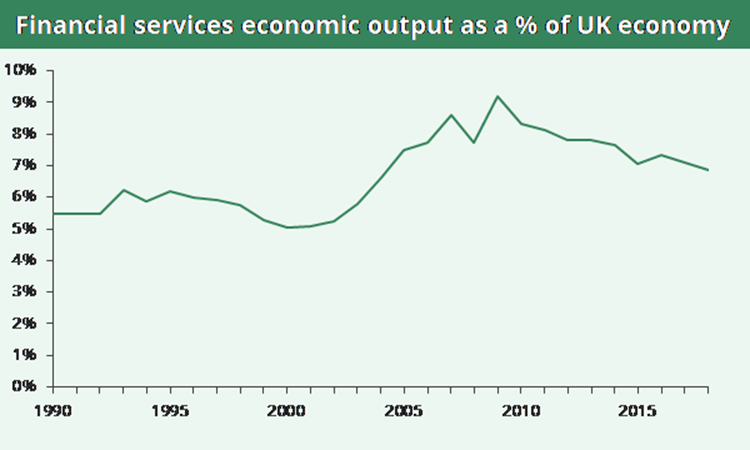
The Financial Sector: Economic Bloat and the Bloated
The financial sector is the source of many of the country's great fortunes, it is also a source of enormous waste. Finance is an intermediate good, like trucking. It is very important to the economy; we need an industry that allocates capital and makes payments. But just as we want as few resources as possible involved in shipping our goods from Point A to Point B, we also want as few resources as possible tied up in the financial sector.
In fact, the financial sector has exploded in size relative to the rest of the economy over the last five decades. We have seen a massive increase in financial transactions, as new financial assets are being constantly created and the existing ones are being traded more frequently. It is difficult to see much gain to the real economy from this explosion in the size and complexity of the financial sector, even if it has meant big fortunes for many people in the sector.
My favorite remedy is a financial transactions tax, which can be thought of as equivalent to the sales tax we impose on most of the goods we buy. A modest tax could easily raise $100 billion a year (0.5 percent of GDP), which would come almost entirely at the expense of the industry.
I find that many people have difficulty understanding how the tax would come at the expense of the industry and not investors. They insist that that banks and brokerage houses will just pass on the tax to investors. This is largely true but it misses the point.
There is considerable research showing that the volume of trading falls roughly in proportion to the increase in the cost of trading. This means that if the cost of trading rises by 40 percent, then the number of shares bought and sold will fall by roughly 40 percent. This means that, for a typical investor, the increase in the cost per trade due to the tax will be offset by the reduction in the number of trades they or their fund manager make.
This means that the total amount that they spend on trading will be little changed, but money they used to pay to the industry for carrying through trades will instead be paid to the government in taxes. Since trades are on net a wash (every trade has a winner and loser, this averages out for all but the most astute investors), investors will not be hurt by a reduction in trading volume.
This one often leaves people baffled, since if they aren't gaining from trading now, they could reduce their volume of trading and save money. That view is correct, they could save money with fewer trades, but nonetheless many people choose to bet that they, or a fund manager will be able to beat the market.
Anyhow, the point here is that if we just applied similar tax treatment to the financial sector as we apply to most goods and services we buy, we would have a radically downsized sector and many fewer great fortunes being earned there.
The other simple quick fix would be to crack down on private equity funds, which are a source of great fortunes for fund partners. My colleague Eileen Appelbaum, along with Rose Batt, has documented many of the abuses the industry has developed to maximize their returns.
In addition to cracking down on abuses, which can get complicated, a simpler issue is that private equity is no longer giving above market returns. In the 1980s and 1990s private equity companies were able to find many underpriced companies, turn them around and make large profits reselling them when they took the company public. This no longer seems to be the case as their returns have largely followed the market since 2006. This means that there is no reason for pension funds, the major source of private equity funding, to be tying up their assets with them.
Even though pension funds may not be gaining by investing with private equity, many of their managers are convinced that they do. There is an easy remedy here. Just require the terms of all contracts of public pension funds with investment managers, including private equity, be posted on the fund's website, showing in clear terms what the managers get paid and the return on the investment. It is likely that the mediocre returns on private equity funds, coupled with the large payments to the private equity managers, would soon discourage pensions from continuing to turn over large amounts of money to these funds.
There are other areas where we can both make the economy more efficient and reduce the opportunities for large fortunes in the financial sector. The most obvious is cleaning up the room for abusive credit practices that the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau was designed to target. There is no economic reason to give clever lawyers and accountants incentives to design ways to rip-off their customers. If these practices are blocked, by regulation or law, it a pure gain for the economy.
As a general rule when it comes to the financial sector, we want it small and we want it simple. If we see lots of resources being devoted to the sector, it is clear indication we have a problem.
Fixing Facebook and Social Media: Treat Them Like Other Media
The battle over Section 230 of the 1996 Communications Decency Act has taken a bizarre turn in recent months because Donald Trump seems to have been convinced that repealing it would mean that Twitter and Facebook couldn't comment on or take down his posts. Actually, the opposite is true. In their current form, without Section 230 protection, Twitter and Facebook would probably be more likely to remove material posted by Donald Trump because it could be libelous and make them subject to legal actions.
But ignoring the Trump confusion, the issue with Section 230 protection is why should Internet outlets be protected from damages, when the exact same material in a traditional print or broadcast outlet could lead to a lawsuit costing millions? Just to be clear, the issue is not directly posted material. If Facebook itself were to post libelous material it would face the same legal liability as the New York Times or CNN. The issue is third party content, where social media companies are completely protected.
If we applied the same rules to Facebook, Twitter, and other social media companies as we do to traditional news outlets (I describe how this could be done in more detail here), we would likely see a radically downsized Facebook and Twitter. There would still be considerable opportunities to make money in this sector, but likely much less than Mark Zuckerberg has made to date.
Even more important than downsizing Mark Zuckerberg's fortune is the issue of democratic control. In both the 2016 and 2020 elections, the public was in the position of begging Mark Zuckerberg to be responsible in the material he was allowing to be spread across his network. We should never be in the position of hoping some billionaire media mogul acts responsibly, with enormous consequences for democracy if they don't. This is a very good argument for breaking up Facebook, so that Mr. Zuckerberg's decisions do not have so much impact on our political process, but repealing Section 230 may get us to the same place through a much simpler mechanism.
Wishing You a Happy and More Egalitarian New Year
Well, that's the list for now. I have other schemes, as my regular readers know, but these are the big ones. The point is that we should never take market outcomes as simple givens. We can structure the market in an infinite number of different ways. Any political strategy that doesn't acknowledge this basic point is doomed to failure.
The post End of the Year Thoughts on Inequality and Its Remedies appeared first on Center for Economic and Policy Research.
-- via my feedly newsfeed