http://stumblingandmumbling.typepad.com/stumbling_and_mumbling/2018/07/capitalism-as-a-fetter.html
I was a little disappointed to see Tony Yates' reaction to Aaron Bastani:
Can we ditch 6th form debates and have someone arguing for evidenced based improvements to our policy portfolio please?
My disappointment is the failure to see that there is, if you like, a third way between utopian communism on the one hand and technocratic tweaks on the other.
It begins from the idea that ten years of stagnant productivity might mean we are now at the phase of capitalism that Marx foresaw:
At a certain stage of development, the material productive forces of society come into conflict with the existing relations of production or – this merely expresses the same thing in legal terms – with the property relations within the framework of which they have operated hitherto. From forms of development of the productive forces these relations turn into their fetters.
If this is the case, then Tony's reply to Aaron is half right. He's right to decry utopianism and demand improvements to our policy portfolio. Where he might err, though, is in not seeing that capitalism itself is the problem. If so, we need quite radical solutions.
So, how might capitalism now be a fetter on the productive forces? Here are a few ways:
First, low investment and innovation might be due in part to the fact that these have external benefits which firms cannot internalize. William Nordhaus famously showed that capitalists capture only a "minuscule fraction" of the benefits of innovation. It might well be that one reason why techno-optimism co-exists with low investment is that firms are loath to invest for fear that their profits will be competed away by future innovations.
Secondly, it's possible that tough intellectual property laws stifle innovation whilst protecting monopolies.
Thirdly, the failure to align managerial and shareholder incentives has led to a lack of productive investment. As Stutz and Kahle have shown, quoted firms today tend to be older and to invest less than their counterparts did years ago. In a similar vein, entrenched management acts as what Joel Mokyr calls a "force of conservatism." Eric Brynjolfsson and Andrew McAfee say that "significant organizational innovation is required to capture the full benefit of…technologies." But bosses lack the incentives or the skills to undertake such innovations.
Fourthly, inequality – not just of income but of workplace power – might itself be a fetter on production. I'm thinking of (at least) three mechanisms here:
- It breeds distrust (pdf). The reduces growth in several ways. It might reduce the many transactions which depend upon trust. The fear of future expropriation or tax increases might deter investment and innovation. It might encourage capitalists to invest in guard labour or in political lobbying to entrench their privilege rather than in productive activity. It can lead to worse policy-making as populism increases because people no longer trust "elites": Brexit might be a consequence of high inequality.
- The high-powered incentives that lead to big CEO salaries can backfire. They encourage dishonesty, reduce creativity and divert management effort from hard-to-monitor tasks such as long-term innovation and towards easier-to-monitor ones such as short-term earnings management.
- Inequalities of wages within the workplace cause dissatisfaction (pdf), which demotivates employees and reduces productivity. Inequalities of power can have the same effect. They demotivate more junior staff, who expect to be told what to do rather than use their initiative. They can also suppress productivity by failing to fully exploit the dispersed fragmentary knowledge of "ground truth" which workers possess.
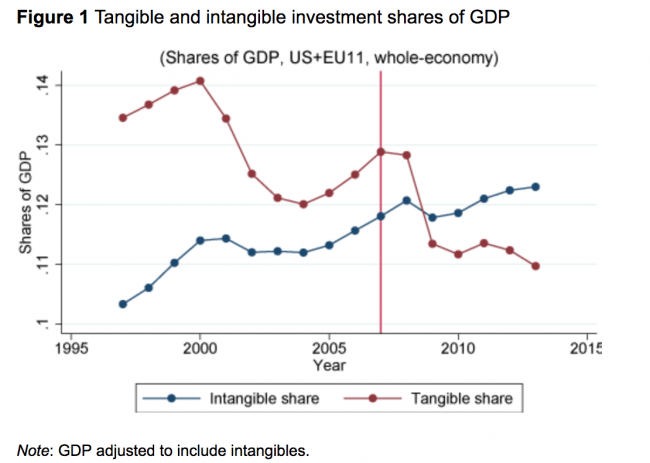
You might wonder: if all this is the case, how did capitalism ever grow? One answer comes from Schumpeter; growth was powered by an entrepreneurial spirit which has been supplanted by bureaucratic management. Another answer is that capitalism has changed. What worked when workers were unskilled drones operating physical machines does not work when skilled immaterial labour works with intangible assets. And thirdly, we must remember that capitalism grew fastest between 1945 and 1973, when it contained a big dollop of social democracy.
If this diagnosis is right, what's the answer? For me, it would comprise a mixture of conventional supply-side policies, state support for innovation and worker coops, and measures to improve workers' bargaining power such as a citizens income and full employment to incentivize labour-saving productivity. You might object that these aren't very socialist. But they should be a stepping stone to socialism, a form of accelerationism. We can't get to a communist utopia overnight.
-- via my feedly newsfeed